Deep Learning: Difference between revisions
| Line 749: | Line 749: | ||
<math>A(\epsilon) \geq 1 - (\frac{\pi}{8})^{1/2} \exp(-\frac{d-1}{2} \epsilon^2)</math> | <math>A(\epsilon) \geq 1 - (\frac{\pi}{8})^{1/2} \exp(-\frac{d-1}{2} \epsilon^2)</math> | ||
As d goes to infinity, the right hand side goes to 1. | As d goes to infinity, the right hand side goes to 1. | ||
In a high-dimensional space, an epsilon expansion will cover almost the entire area. | |||
;Theorem | ;Theorem | ||
c-class classification | c-class classification | ||
<math>\rho_c, u_c | <math>\rho_c, u_c</math> | ||
<math>f_c = \mu_1 \{x \mid | <math>v_c=\delta_{n-1} * u_c</math> is the max density relative to uniform density. | ||
<math>f_c = \mu_1 \{x \mid C(x)=c\}</math> is the area where the classifier <math>C</math> classifies as class c. | |||
Pick a class <math>f_c \leq \frac{1}{2}</math>. | Pick a class <math>f_c \leq \frac{1}{2}</math>. | ||
Sample x from <math>\rho_c</math>. | Sample x from <math>\rho_c</math>. | ||
Revision as of 00:34, 4 October 2020
Notes for CMSC 828W: Foundations of Deep Learning (Fall 2020) taught by Soheil Feizi.
Basics
A refresher of Machine Learning and Supervised Learning.
Empirical risk minimization (ERM)
Minimize loss function over your data: \(\displaystyle \min_{W} \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} l(f_{W}(x_i), y_i))\)
Loss functions
For regression, can use quadratic loss: \(\displaystyle l(f_W(x), y) = \frac{1}{2}\Vert f_W(x)-y \Vert^2\)
For 2-way classification, can use hinge-loss: \(\displaystyle l(f_W(x), y) = \max(0, 1-yf_W(x))\)
For multi-way classification, can use cross-entropy loss:
\(\displaystyle g(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}\)
\(\displaystyle \min_{W} \left[-\sum_{i=1}^{N}\left[y_i\log(y(f_W(x_i)) + (1-y_i)\log(1-g(f_W(x_i))\right] \right]\)
Nonlinear functions
Given an activation function \(\phi()\), \(\phi w^tx + b\) is a nonlinear function.
Models
Multi-layer perceptron (MLP): Fully-connected feed-forward network.
Optimization
Apply gradient descent or stochastic gradient descent to find \(W^*\).
Stochastic GD:
- Sample some batch \(B\)
- \(w^{(t+1)} = w^{(t)} - \eta \frac{1}{|B|} \sum_{i \in B} \nabla_{W} l(f_{W}(x_i), y_i)\)
Optimizers/Solvers:
- Momentum
- RMSProp
- Adam
DL Optimization
(Lectures 2-3, September 3)
The role of "over-parameterization".
In general, you can have poor local minimums and saddle points (with pos+neg Hessian).
However, in practice GD & SGD work pretty well.
Lecture 2 (Sept 3) is about Liu et al. [1].
Suppose we have a classification problem with \(c\) labels and \(N\) samples total. This gives us \(n=N*c\) constraints.
Interpolation is possible if the number of parameters \(m\) is greater than the number of samples \(n=N*c\).
This is called the over-parameterized regime.
In the exact interpolation regime, we have: \[ \begin{aligned} f_W(x_1) &= y_1 = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ \vdots \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^c\\ &\vdots\\ f_W(x_1) &= y_1 = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ \vdots \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^c\\ \end{aligned} \] This can be rewritten as \(\displaystyle F(w)=y\) where x is implicit.
In the under-parameterized regime, we get poor locals. (See Fig 1a of [1]).
The poor-locals are locally convex in the under-parameterized regime but not in the over-parameterized.
Over-parameterized models have essential non-convexity in their loss landscape.
Minimizers of convex functions form convex sets.
Manifold of \(w^*\) have some curvature.
Manifold of \(w^*\) should be an affine subspace. This is in general for non-linear functions.
So we cannot rely on convex analysis to understand over-parameterized systems.
Instead of convexity, we use PL-condition (Polyak-Lojasiewicz, 1963):
For \(\displaystyle w \in B\), \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\Vert \nabla L(w) \Vert^2 \geq \mu L(w)\) which implies exponential (linear) convergence of GD.
Tangent Kernels
Suppose our model is \(F(w)=y\) where \(w \in \mathbb{R}^m\) and \(y \in \mathbb{R}^n\).
Then our tangent kernel is:
\[K(w) = \nabla F(w) \nabla F(w)^T \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\]
where \(\nabla F(w) \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times m}\)
Theorem 4.1 (Uniform conditioning implies PL* condition)
If \(\lambda_{\min} (K(w)) \geq \mu\) then \(\mu\text{-PL*}\) on \(B\).
\(\displaystyle \begin{aligned} \frac{1}{2}\Vert \nabla f(w) \Vert^2 &= \frac{1}{2}\Vert (F(w)-y)^T \nabla F(w)\Vert^2\\ &=\frac{1}{2}(F(w)=y)^T \nabla F(w) \nabla F(w)^T (F(w)-y)\\ &\geq \frac{1}{2} \lambda_{\min}(K(w)) \Vert F(w)-y\Vert ^2\\ &= \lambda_{\min}(K(w)) L(w)\\ &\geq \mu L(w) \end{aligned} \)
Informal convergence result:
GD converges exp fast to a solution with the rate controlled by a condition number:
\[ \kappa_{F} = \frac{\sup_{B} \lambda_{\max}(H)}{\inf_{B} \lambda_{\min}(K)}\]
Ideally we want this to be small.
\(\displaystyle F(w) = Aw = y \in \mathbb{R}^n\)
\(\displaystyle L(w) = \frac{1}{2} \Vert Aw-y\Vert^2\)
Our tangent kernel is:
\(\displaystyle K(w)=AA^T\)
and our hessian is \(\displaystyle H=A^TA\).
\(\displaystyle \kappa_{F} = \frac{\lambda_{\max}(K)}{\lambda_{\min}(K)} \geq 1\).
Our intuition is:
\(\displaystyle K=AA^T \implies E[\log K_F] \approx \log(\frac{M}{|m-n|+1})\).
So as \(\displaystyle m \to \infty\), \(\displaystyle \kappa_{F} \to 1\).
Theorem 4.2 (Local PL* implies existence of a solution + fast convergence)
Assume \(\displaystyle L(w)\) is \(\beta\)-smooth and satisfies \(\mu\)-PL condition around a ball \(\displaystyle B(w_0, R)\) with \(\displaystyle R = \frac{2\sqrt{w\beta L(w_0)}{\mu}\). Then:
- Existence of a solution: There exists a global minimum of \(\displaystyle L\), \(\displaystyle \mathbf{w}^* \in B(\mathbf{w}_0, R)\) s.t. \(\displaystyle F(\mathbf{w}^*)=\mathbf{y}\).
- Convergence of GD: GD with step size \(\displaystyle \eta = 1/\sup_{\mathbf{w}}\lambda_{\max}(H)\) converges with exponential convergence rate:
- \[L(w_t) \leq \left(1-\kappa^{-1}(B(\mathbf{w}, R))\right)^t L(\mathbf{w}_0)\]
We want to prove:
- A solution exists.
- \(\displaystyle L(w_t) \leq (1-\eta \mu)^t L(w_0)\)
Note that \(\displaystyle \eta \mu\) is the inverse of the condition number.
Beginning of Lecture 3 (September 8, 2020)
Last time (lecture 2) we expect zero training error from overparameterization.
This is the interpolation regime.
Here the number of parameters \(m\) is greater than the number of samples \(n=Nc\).
Here the manifold of \(w^*\) is the intersection of functions where \(F(w, x_1)=Y_1\) and \(F(w,x_2)=Y_2\).
Assume we use squared loss \(L(w)=\frac{1}{2}\Vert F(w)-Y \Vert^2\).
In general, our loss function is non convex, even locally.
PL-condition: If the magnitude of gradient is greater than a constant multiple \(\mu\) of loss then we say it is \(\mu\)-PL.
If our loss satisfies PL and some other conditions, then it will converge with gradient descent.
Intuition of PL
Assume:
- Loss \(\displaystyle L(w)_{w \in B}\) is \(\mu\)-PL
- Loss is \(\beta\)-smooth
- The hessian is bounded by \(\beta\)
- \(\eta=\frac{1}{\beta}\)
- Assume gradient descent: \(w_{t+1}=w_t-\mu \nabla L(w_t)\)
By Taylor's expansion:
\[
\begin{aligned}
L(w_{t+1}) &= L(w_t) + (w_{t+1}-w_t)^T \nabla f(w_t) + \frac{1}{2}(w_{t+1}-w_t)^T H(w')(w_{t+1}-w_{t})\\
&=L(w_t) + (-\eta)\nabla L(w_t)^T \nabla f(w_t) + \frac{1}{2}(-\eta)\nabla L(w_t)^T H(w')(-\eta) \nabla L(w_t)\\
&\leq L(w_t) - \eta \Vert \nabla L(w_t) \Vert^2 + \frac{\eta^2}{2} \nabla L(w_t)^T H(w') \nabla L(w_t)\\
&\leq L(w_t) - \eta \Vert \nabla L(w_t) \Vert^2 (1-\frac{\eta \beta}{2}) &\text{by assumption 3}\\
&\leq L(w_t) - \frac{\eta}{2} \Vert \nabla L(w_t) \Vert^2 &\text{by assumption 4}\\
&\leq L(w_t) - \eta \mu L(w_t) &\text{by }\mu\text{-PL assumption}\\
&= (1-\eta \mu)L(w_t)
\end{aligned}
\]
This implies our loss at any iteration is \(\displaystyle L(w_t) \leq (1-\eta \mu)^t L(w_0)\).
Thus we see a geometric or exponential decrease in our loss function with convergence rate \(\displaystyle (1-\eta \mu)\).
Similar results hold for SGD.
If we don't have convergence, we're not sure if this means we're violating the \(\mu\)-PL condition.
It is possible one of the other assumptions is violated (e.g. if learning rate is too large).
These arguments should hold for ReLU networks since the non-differentiable points are measure 0 but it would require a more careful analysis.
Caveat:
Here we assume our loss is in a ball \(\displaystyle B(w_0, R) = \{w | \Vert w - w_0 \Vert \leq R\}\) where \(\displaystyle R \leq \frac{2\sqrt{2 \beta L(w_0)}}{\mu}\).
We need to show that our gradient updates never causes us to leave this ball.
The lengths of the update vectors are \(\displaystyle \Vert w_{t+1} - w_{t}\Vert = \eta \Vert \nabla L(w_t)\Vert\).
To show that we never leave the ball, we need to have an upper bound on the length of our gradients \(\displaystyle \Vert \nabla L(w_t) \Vert\).
There is a tradeoff because for PL, we want a large \(\displaystyle \mu\) to lower bound the gradients but that would require satisfying PL over a large ball. If \(\displaystyle \mu\) is small, then we have fast (large) updates but over a small ball.
From the proof above, we have:
\(\displaystyle L(w_{t+1}) \leq L(w_t) - \frac{\eta}{2} \Vert \nabla L(w_t) \Vert^2\).
We can use this to prove we are in the ball.
Why do neural networks satisfy the conditioning assumptions?
Hessian Control
We can show \(mu\)-PL by showing the smallest eigenvalue of the tangent kernel is bounded: \(\displaystyle \lambda_{\min}(K(w_0)) \geq \mu\) and \(\displaystyle \sup_{B} \Vert H(F)\Vert\).
The tangent kernel is \(\displaystyle \nabla F(w) \nabla F(w)^T\).
If hessian is bounded then gradients don't change too fast so if we are \(\displaystyle \mu\)-PL at the initialization then we are \(\displaystyle \mu\)-PL in a ball around the initialization.
Suppose we have a NN: \(\displaystyle x \in \mathbb{R} \to y\).
\(\displaystyle f(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}}\sum_{i=1}^{m} v_i \sigma(w_i, x)\).
- Can we prove convergence of GD for this NN?
\(\displaystyle \nabla_{w_i} f(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} v_i x \sigma'(w_i x)\)
\(\displaystyle K(w, x_j, x_j) = \frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m} v_i^2 x^2 \left(\sigma'(w_i x)\right)^2 \equiv O(1)\) are the j-th diagonal terms of the tangent kernel:
\(\displaystyle K(w) \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\).
Then the trace of the tangent kernel is also \(\displaystyle O(1)\) so the eigenvalues are bounded: \(\displaystyle \Vert K(w) \Vert = O(1)\).
\(\displaystyle H_{ij} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} v_i \sigma '' (w_j x) x^2 1_{i=j}\)
The hessian is a diagonal matrix. The spectral norm of the hessian (the maximum eigenvalue) is the maximum of the diagonal elements:\\
\(\displaystyle \Vert H \Vert_2 = \max_{i \in [m]} H_{ii} = \frac{x^2}{\sqrt{m}} \max_{i \in [m]} | v_i \sigma '' (w_j x)| = O(\frac{1}{\sqrt{m}})\)
As m goes to infinity, our hessian \(\displaystyle H\) goes to 0 and tangent kernel \(\displaystyle K\) goes to a constant.
Thus Hessian control implies convergence of GD/SGD.
- However this argument assumes the model is almost linear.
- This hessian control can be extended to L-layer NN with \(\displaystyle m=\omega(\frac{n}{\mu})\)
Example:
\(\displaystyle g(w, x) = \phi(\frac{1}{\sqrt{m}}\sum_{i=1}^{m}v_i \sigma(w_i x))\)
then
- \(\displaystyle \Vert K(w) \Vert = O(1)\)
- \(\displaystyle \Vert H \Vert = O(1)\) if \(\displaystyle (\phi'' \neq 0)\)
so we cannot use hessian control.
- Lemma
If f is mu-PL then \(\displaystyle \phi \circ f\) is \(\displaystyle \mu \rho^2\)-PL (\(\displaystyle | \phi'(f(w,x))| \gt \phi\)).
implies \(\displaystyle L(w_t) \leq (1- \eta \mu \rho^2)L(w_0)\).
GD converges even though our model does not go to a linear model.
Takeaway
Over-parameterization does not lead to linearization. Over-parameterization leads to good conditioning which leads to PL and convergence of GD/SGD.
Other papers:
- Simon Du et al.[2]
Start of Lecture 4 (Sept 10)
This lecture is about Soudry et al.[3].
Setup:
- Binary classification
- Data is linearly separable
- No bias term (b=0)
Why do we pick \(w^*\) to be the max-margin solution?
To have better generalization.
We will consider functions \(f_w(x) = w^t x\) where we have \(\{(x_i, y_i)\}_{1}^{N}\), \(f_w: \mathbb{R}^d \to \mathbb{R}\), \(x_i \in \mathbb{R}^d\) and \(y_i \in \{-1, 1\}\).
We can use one of the loss functions:
- hinge loss \(l(x)=\max(1-x, 0\))
- logistic loss \(l(u) = \log(1+e^{-u})\)
- exp loss \(l(u)=e^{-u}\)
Our overall loss will be the sum of loss for each sample:
\(L(w) = \sum_{u=1}^{N}l(y_i w^t x_i)\)
Here \(x_i\) and \(y_i\) are constants so call \(\tilde{x}_i = y_i x_i\).
Now our loss is \(L(w) = \sum_{u=1}^{N}l(w^t \tilde{x}_i)\)
Assumptions:
- Data is linearly separable: \(\exists w^* \) s.t. \((w^*)^t x_i > 0\).
- \(l(u)\) is positive, differentiable, monotonically decreasing to 0, and \(\beta\)-smooth.
- Logistic and exp loss satisfy assumption 2.
Hard SVM:
Call the SVM solution \(w_{svm}^t x = 0\).
Recall the SVM optimization is:
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
\min &\Vert w \Vert^2\\
&w^t x_i \geq 1 \; \forall i
\end{aligned}
\)
We use GD to find \(w^*\):
\(\min \sum_{i=1}^{N} l(w^t x_i)\)
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
w(t+1) &= w(t) - \eta \nabla L(w(t))\\
&= w(t) - \eta \sum_{i=1}^{N} l'(w^t x_i) x_i
\end{aligned}
\)
Since the data is linearly separable, there exists \(w^*\) such that:
\((w^*)^t \nabla L(w) = \sum_{i=1}^{N} l'(w^t x_i) x_i^t w^* < 0\)
Here \(l'(w^t x_i) > 0\) and \(x_i^t w^* < 0\).
This implies there are no finite critical points (where \(\nabla L(w) = 0\).
But GD on a smooth loss converges to a critical point.
This implies \(\Vert w(t) \Vert\) goes to infinity and the loss converges to 0.
Since the loss converges to 0, GD converges to a global min.
Assumption 3: Loss function has exponential tails.
Exp and logistic loss satisfy this assumption.
- Theorem
Under assumptions 1-3, GD behaves as:
\(\displaystyle w(t) = w_{svm} \log(t) + \rho(t)\) where \(\displaystyle \Vert \rho(t) \Vert = o(\log \log t)\).
This implies \(\displaystyle \lim_{t \to \infty} \frac{w(t)}{\Vert w(t) \Vert} = \frac{w_{svm}}{\Vert w_{svm} \Vert}\).
Consider exponential loss:
\(\displaystyle l(u) = e^{-u}\)
GD in the asymptotic regime: \(\displaystyle w(t)^t x_i \to \infty\).
Lets assume the normalized w converges to a limit point \(\displaystyle w_{\infty}\):
\(\displaystyle \frac{w(t)}{\Vert w(i) \Vert} \to w_{\infty}\).
This implies \(\displaystyle w(t) = g(t) w_{\infty} + \rho(t)\).
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
-\nabla L(w) &= \sum_{i=1}^{N} \exp(-w(t)^t x_i) x_i\\
&\to \sum_{i=1}^{N} \exp(-g(t)w_{\infty}^t x_i) x_i\\
\end{aligned}
\)
Here \(\displaystyle -g(t) w_{\infty}^t x_i\) go to negative infinity since \(\displaystyle g(t) \to \infty\).
Only samples with smallest \(\displaystyle w_{\infty}^t x_i\) will contribute to the gradient:
\(\displaystyle \operatorname{argmin}_{i} w_{\infty}^t x_i\) which are exactly the support vectors.
Thus:
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
&& -\nabla L(w) &= \sum_{i \in SV} \alpha_i' x_i\\
\implies && w_{\infty} &= \sum_{i \in SV} \alpha_i'' x_i
\end{aligned}
\)
\(\displaystyle \begin{aligned} \hat{w} &= \sum_{i}^{N} \alpha_i x_i\\ \alpha_i&= 0 & x_i \notin SV\\ \alpha_i &\neq 0 & x_i \in SV\\ \end{aligned} \) These are the KKT conditions for SVM. \(\displaystyle \implies \frac{w_\infty}{\Vert w_\infty \Vert} = \frac{w_{SVM}}{\Vert w_{SVM} \Vert} \)
Rate of convergence is very slow:
\(\displaystyle \left\Vert \frac{w(t)}{\Vert w(t) \Vert} - \frac{w_{SVM}}{\Vert w_{SVM} \Vert } \right\Vert = O(\frac{1}{\log(t)})\)
Takeaway
- Even when the loss is very small, if we continue GD optimization we approach the max-margin solution which improves generalization.
- Validation or test loss may go to infinity \(\displaystyle \Omega(\log (t))\). It is better to look at the classification error in test/validation rather than the pure loss value.
- Even if validation loss is increasing, you should not stop GD because it will approach max-margin.
- More recent work
- Implicit bias exists in over-parameterized neural networks.
- Experimentally, Adam and Adagrad do not have implicit bias but have worse generalization error.
DL Generalization
Beginning of Lecture 5 (September 15, 2020).
Training set \(S = \{z^{(i)} = (x^{(i)}, y^{(i)}) \}_{i=1}^{n}\).
Our samples are from some unknown distribution: \(Z^{(i)} = (x^{(i)}, y^{(i)}) \sim P_{X, Y}\).
\(\min_{h \in H} L_{S}(h) \to h_{S}^{*}\)
In practice, we cannot compute our population loss: \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h) = E_{z \in P_{X, Y}} [l(h, z)]\).
\(\displaystyle \min{h \in H} L_{D}(h) \to h_{D}^*\).
The goal is to learn something from the training set which has a low population loss.
The estimation error is \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_{S}^*) - L_{D}(h_{D}^*)\) where \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_s^*)\) is the true population loss of the hypothesis gained from the test set and \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_D^*)\) is the minimum population loss.
Classical Learning Theory
If \(\displaystyle \forall P_{X, Y}, n \geq n_0\), \(\displaystyle Pr(L_{D}(h_{S}^*) - L_{D}(h_{D}^*) \leq \epsilon) \geq 1-\delta\) then is H called PAC-learnable.
Bias-variance tradeoff
\(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_{S}^*) = L_{D}(h_{D}^*) + [L_{D}(h_{S}^*) - L_{D}(h_{D}^*)]\)
- \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_{D}^*)\) is called the bias term, the loss of the best hypothesis in your hypothesis class. If the complexity of \(\displaystyle H\) increases, then the bias term will decrease.
- \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_{S}^*) - L_{D}(h_{D}^*)\) is the estimation error or variance term.
- As the complexity of \(\displaystyle H\) increases, the bias decreases but the variance increases.
However, this view is not complete.
- Notations
\(\displaystyle f = l \circ h\)
\(\displaystyle L_{S}(h) = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} f(z^{(i)})\)
\(\displaystyle L_{D}(h) = E_{Z \sim P_{X, Y}}[ f(z) ] \)
\(\displaystyle F = l \circ H = \{ l \circ h, \forall h \in H \}\)
\(\displaystyle F \circ S = \left\{
\begin{bmatrix}
f(z^{(1)})\\
\vdots\\
f(z^{(n)})
\end{bmatrix}, \forall f \in F \right\}\)
Generalization error: \(\displaystyle L_{D}(h_{S}^*) - L_{S}(h_{S}^*)\)
We want to have a uniform bound on this error: \(\displaystyle G = \sup_{h \in H} L_{D}(h) - L_{S}(h)\).
We don't have the population distribution \(\displaystyle D\).
Instead, what we do is split the training data: \(\displaystyle S = S_1, \cup S_2\) with \(\displaystyle |S_1|=|S_2|=\frac{n}{2}\).
Now we have:
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
G \approx G' &=\sup_{h \in H} L_{S_1}(h) - L_{S_2}(h)\\
&= \sup_{h \in H} F(s_1) - F(s_2)\\
&= \sup_{h \in H} \frac{1}{n/2} \sum_{z^{(i)} \in S_1} f(z^{(i)}) - \frac{1}{n/2} \sum_{z^{(i)} \in S_1} f(z^{(i)})\\
&= \sup_{h \in H} \frac{2}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sigma_i f(z^{(i)}) & \text{where }\sigma_{i} = I[z^{(i)} \in S_1] - I[z^{(i)} \in S_2]
\end{aligned}
\)
We can use randomized partitioning such that \(\displaystyle \sigma = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{w.p. }1/2\\ -1 & \text{w.p. }1/2 \end{cases} \)
\(\displaystyle G \approx E_{\sigma}[G'] = \frac{2}{n} E_{\sigma} \left[ \sup_{h \in H} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sigma_i f(z^{(i)}) \right]\)
\(\displaystyle R(A) = \frac{1}{n} E_{\sigma} \left[ \sup _a \in A \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sigma_i a_i \right]\) is called the Rademacher complexity.
Setting \(\displaystyle A = \{a_i\} = F \circ S\) \(\displaystyle \implies G \approx 2 R(F \circ S)\)
Theorem
With probability \(\displaystyle 1 - \delta\),
\(\displaystyle L_D(h) - L_{S}(h) \leq 2 R(F \circ S) + c \sqrt{\frac{\log(4/\delta)}{n}}\)
Example: \(\displaystyle H = \{ h(x) = w^t x, \Vert w \Vert_2 \leq 1\}\)
\(\displaystyle R(H \circ S) \leq \frac{\max_i \Vert x^{(i)} \Vert_2}{\sqrt{n}}\)
Question: What is the Rademacher complexity of a deep model?
\(\displaystyle H = \{ h(x) \mid h \text{ is a NN with some structure}\}\)
If \(\displaystyle R(H \circ S)\) is small then by the theorem, we can have good generalization performance.
Zhang et al.[4] perform a randomization test.
They assign random labels and observe that neural networks can fit random labels.
Recall \(\displaystyle R(H \circ S) = \frac{1}{n} E_{\sigma} \left[ \sup_{h \in H} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sigma_i h(x_i) \right] \approx 1\)
This shows that Rademacher complexity and VC-dimension are not useful for explaining generalization for neural networks.
Theorem
There exists a two-layer NN with Relu activations and \(\displaystyle 2n+d\) parameters that can represent any function on a sample size \(\displaystyle n\) in d dimensions.
Lecture 9 (Sept 17)
From previous lecture (Zhang et al.[4]), we see that NN optimization is not much more difficult training on random labels in terms of convergence rate. Thus, Rademacher complexity and VC dimension cannot explain generalization by itself.
Examples of explicit regularization:
- Data augmentation (e.g. random crop)
- Weight decay (L2 regularization on parameters)
- Dropout
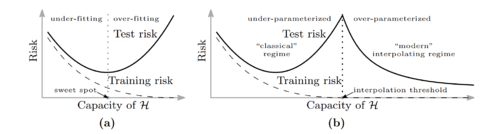
These types of explicit regularization improves generalization, but models still generalize well without them.
One reason would be implicit regularization by SGD.
Belkin et al.[5] observe that as models get more over-parameterized in the interpolation regime, test error will begin decreasing with the number of parameters. This is called double descent.
- Intuition
- In the over-parameterized regime, there are infinitely many solutions in the manifold of \(\displaystyle f_{w^*}\).
For SGD, it is easier to find simple solutions (e.g. functions with small norms). This leads to better generalization.
Can we analyze the double descent curve for some simple distributions or models?
Setup:
Our features are \(\displaystyle x = (x_1,..., x_d)\) where \(\displaystyle x_i\) are from standard normal.
Our labels are \(\displaystyle y = x^t \beta\). This is the noise-free case.
Our training set: \(\displaystyle \{(x^{(i)}, y^{(i)})\}_{i=1}^{n}\) written as \(\displaystyle X =
\begin{pmatrix}
(x^{(1)})^t\\
\vdots\\
(x^{(n)})^t
\end{pmatrix}
\)
Learning: We select \(\displaystyle p\) features: \(\displaystyle T \subseteq [d]\), \(\displaystyle |T| = P\) and fit a linear model \(\displaystyle \beta^{*}_{T} \in \mathbb{R}^{p}\), \(\displaystyle \beta^*_{T^c} =0\). Here \(\displaystyle T^c\) is the set of features we are not using.
Define \(\displaystyle X_{T} = \begin{pmatrix} (x^{(1)}_T)^t\\ \vdots\\ (x^{(n)}_T)^t \end{pmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times P} \)
Quadratic loss: \(\displaystyle \min_{\beta_T} \Vert X_T \beta_T - y \Vert_{2}^{2} \in \mathbb{R}\).
The optimal solution is \(\displaystyle \beta_{T}^* = (X_{T}^t X_{T})^{-1} X_{T}^t y = X_{T}^{+} y\) where \(\displaystyle X_{T}^{+}\) is the Moore-penrose Pseudo-inverse.
Since we know \(\displaystyle P_{X, Y}\), we can compute the generalization error exactly.
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
E_{X,Y} \left[(y - x^t \beta^*)^2 \right] &= E \left[(x^t(\beta - \beta^*))^2\right]\\
&= E \left[(\beta - \beta^*)^t x x^t (\beta - \beta^2)\right]\\
&= (\beta - \beta^*)^t E \left[ x x^t \right] (\beta - \beta^2)\\
&= \Vert \beta - \beta^* \Vert\\
&= \Vert \beta_{T^c} \Vert^2 + \Vert \beta_{T} - \beta_{T}^* \Vert^2
\end{aligned}
\)
- Theorem
- \(\displaystyle B_{T^c} \neq 0\)
\(\displaystyle E \left[(y - x^t \beta^*)^2 \right] = \begin{cases} \Vert B_{T^C} \Vert^2 (1 + \frac{p}{n-p-1}) & p \leq n-2\\ +\infty & n-1 \leq p \leq n+1\\ \Vert B_{T} \Vert ^2 (1 - \frac{n}{p}) + \Vert B_{T^c} \Vert^2 (1 + \frac{n}{p-n-1}) & p \geq n+2 \end{cases} \)
In other cases, prescient feature selection. We can include features in \(\displaystyle T\) by decreasing the order of \(\displaystyle \beta_j^2 = \frac{1}{j^2}\). From this we get a behavior like double descent.
Related Works
Jiang et al.[6] provide some emperical evaluations of different generalization bounds such as:
- Sharpness-based bounds (PAC-Bayesian)
- Norm-based bounds
Neural Tangent Kernels (NTKs)
Beginning of Lecture 7 (Sept. 22, 2020)
Linear Regression
Assume we have a dataset:
\(\displaystyle \{(x_i, y_i)\}_{i=1}^{n}\)
\(\displaystyle y_i \in \mathbb{R}\)
\(\displaystyle x_i \in \mathbb{R}^d\)
\(\displaystyle f(w, x) = w^t x\)
\(\displaystyle L(w) = \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_i - f(w, x_i))^2\)
\(\displaystyle \min_{W} L(w)\)
GD: \(\displaystyle w(t+1) = w(t) - \eta_{t} \nabla L(w_t)\) where our gradient is:
\(\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_i - f(w, x_i)) \nabla_{w} f(w_t, x_i) = \sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_i - f(w, x_i)) x_i\)
Kernel Method
\(\displaystyle x_i \in \mathbb{R}^d \to \phi(x_i) \in \mathbb{R}^{D}\) with \(\displaystyle D \gt \gt d\)
Suppose \(\displaystyle d=3\) and \(\displaystyle x = \begin{bmatrix} x_1\\x_2\\x_3 \end{bmatrix} \to \phi(x)= \begin{bmatrix} x_1\\ x_2\\ x_3\\ x_1 x_2\\ x_1 x_3\\ x_2 x_3 \end{bmatrix} \)
\(\displaystyle f(w, x) = w^t \phi(x)\)
Is this model linear in w? Yes!
Is this model linear in x? No!
\(\displaystyle \min \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n} (y_i - w^t \phi(x_i))^2\)
Apply GD or convex optimization.
Q: What is the issue here?
- \(\displaystyle \phi\) is fixed!
- \(\displaystyle D = O(d^k)\)
- For ImageNet, d is approx \(\displaystyle 10^5\) so \(\displaystyle D=O(10^15)\)
- Kernel Trick
We may have a closed form solution for \(\displaystyle \langle \phi(x_i), \phi(x_j) \rangle\).
This is called the kernel function \(\displaystyle K(x_i, x_j)\) or kernel matrix \(\displaystyle K \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\).
K is a PSD matrix.
Idea: In many cases without "explicit" comp of \(\displaystyle \phi(x_i)\), we can compute \(\displaystyle K(x_i, x_j)\).
- Polynomial Kernels
\(\displaystyle K(x_i, x_j) = (x + x_i^t x_j)^k\) with \(\displaystyle \phi(x_i) \in \mathbb{R}^D\)
Here \(\displaystyle D=O(d^k)\) but \(\displaystyle K(x_i, x_j)\) is \(\displaystyle O(d)\).
Many classical techniques can be kernelized:
SVM to Kernel SVM
Ridge regression to Kernel ridge regression
PCA to Kernel PCA
Neural Networks
Consider a two-layer neural network.
We can write the output as:
\(\displaystyle y = f(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} \sum_{i=1}^{m} b_i \sigma(a_i^t x)\)
We use quadratic loss: \(\displaystyle L(w) = \frac{1}{2} \sum_{i=1}^{n} (f(w, x_i) - y_i)^2\)
GD: \(\displaystyle w(t+1) = w(t) - \eta_{t} \sum_{i=1}^{n} (f(w, x_i) - y_i) \nabla_w f(w_t, x_i)\)
Init N(0,1)
Our weights update along a trajectory: w(0), w(1), ...
Each \(\displaystyle w\) is a weight matrix.
Empirical Observation: When the width of the network \(\displaystyle m\) is large, the trajectory of the gradient descent is almost static.
This is called lazy training.
- Not always the case! Especially for small \(\displaystyle m\).
Since the change in the model weights are not large, we can write the first-order taylor approximation:
\(\displaystyle f(w, x) \approx f(w_0, x) + \nabla_{w} f(w_0, x)^t (w - w_x) + ...\)
This model is linear in \(\displaystyle w\).
\(\displaystyle \phi(x) = \nabla_{w} f(w_0, x)\)
The kernel \(\displaystyle K = \langle \phi(x_i), \phi(x_j) \rangle\) is called the Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK).
Go back to our 2-layer NN:
\(\displaystyle f_m(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} \sum b_i \sigma(a_i^t x)\)
\(\displaystyle \nabla_{a_i} f_m(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} b_i \sigma'(a_i^t x) x\)
\(\displaystyle \nabla_{b_i} f_m(w, x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{m}} \sigma(a_i^t x)\)
\(\displaystyle K_{m}(x, x') = K_{m}^{(a)}(x, x') + K_{m}^{(b)}(x, x')\)
\(\displaystyle K_{m}^{(a)}(x, x') = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} b_i^2 \sigma'(a_i^tx) \sigma'(a_i^tx) (x x')\)
\(\displaystyle K_{m}^{(b)}(x, x') = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sigma(a_i^t x) \sigma(a_i^t x')\)
- \(\displaystyle a_i\) and \(\displaystyle b_i\) are independent samples at initialization.
Based on law of large numbers, as m goes to infinity,
\(\displaystyle K_{m}^{(a)}(x, x') \to K^{(a)}(x, x') = E \left[ b^2 \sigma'(a^t x) \sigma'(a^t x') (x x') \right]\)
\(\displaystyle K_{m}^{(b)}(x, x') \to K^{(b)}(x, x') = E \left[ \sigma(a^t x) \sigma(a^t x') \right]\)
\(\displaystyle K^{(a)}(x, x') = \frac{(x x') E[b^2]}{2 \pi} (\pi - \theta(x, x))\)
\(\displaystyle K^{(b)}(x, x') = \frac{\Vert x \Vert \Vert x' \Vert E[\Vert a \Vert^2]}{2 \pi d} ((\pi - \theta(x, x')) \cos(\theta) + \sin \theta)\)
- Q
- When is this taylor approximation good?
If the Hessian has bounded eigenvalues. (Hessian Control)
- Analyze GD
\(\displaystyle \eta \to 0\) Gradient-flow
\(\displaystyle w(t+1) = w(t) - \eta \nabla_{w} L(w(t)) \implies \frac{w(t+1) - w(t)}{\eta} = - \nabla_{w} L(w(t))\)
\(\displaystyle \to \frac{dw(t)}{dt} = -\nabla_{w} L(w(t))\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{dw(t)}{dt} = -\nabla_{w} \hat{y}(w) (\hat{y}(w) - y)\)
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
\frac{d\hat{y}(w(t)}{dt} &= - \nabla_{w} \hat{y}(w(t))^2 \frac{dw(t)}{dt} \\
&= - \nabla_{w} \hat{y}(w(t))^2 \nabla_{w} \hat{y}(w) (\hat{y}(w) - y)\\
&\approx -K(w_0) (\hat{y}(w(t))-y)
\end{aligned}
\)
If we let \(\displaystyle u = \hat{y} - y\), then \(\displaystyle \frac{du}{dt} \approx -K(w_i) u\).
This ODE implies \(\displaystyle u(t) = u(0)\exp(-K(w_i)t)\).
In the over-parameterized case, \(\displaystyle K(w_0) \gt 0 \) (positive definite).
- SOTA NNs often outperform kernel methods (even based on NTKs)
Adversarial Robustness
Beginning of Lecture 8 (Sept. 24 2020)
In standard ERM, we have a dataset:
\(\displaystyle \{(x_i, y_i)\}_{i=1}^{n}\) where \(\displaystyle x_i \in \mathbb{R}^d\) and \(\displaystyle y_i \in [c]\)
We optimize \(\displaystyle \min_{\theta} E \left[ l(f_{\theta}(x), y) \right] = \frac{1}{n} \sum l(f_{\theta}(x_i), y_i) \).
- What is an adversarial example?
\(\displaystyle x'\) is an adversarial example for \(\displaystyle x\) under a model \(\displaystyle f_{\theta}()\) if
- \(\displaystyle f_{\theta}(x) \neq f_{\theta}(x')\) and
- \(\displaystyle f_{human}(x) = f_{human}(x)\)
One key challenge is that we don't have a precise definition of human perception.
Formulation
Threat Models: \(\displaystyle x' \in T(x, \epsilon)\)
Example: Lp model \(\displaystyle \{x' | \Vert x' - x \Vert_{lp} \leq \epsilon \}\)
Non-Lp threat models:
One problem with Lp models is that two identical images can have large L2 difference. For example, shifting or rotating an image.
An example of a non-Lp threat model is using Wasserstein difference.
Attacks
The goal is given \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle f_{\theta}()\), we want to compute \(\displaystyle x'\) such that \(\displaystyle c* = f_{\theta}(x) \neq f_{\theta}(x')\).
- Targeted: Given a target label \(\displaystyle t \neq c^*\), \(\displaystyle f_{\theta}(x') = t\).
- Untargeted: \(\displaystyle c^*\) is not given
We mostly focus on targeted attacks.
- White-box: Adversary knows everything
- Black-box: Adversary has limited knowledge
We mostly focus on white-box attacks.
- Inference-time (evasion) attacks
- Training-time (poison) attacks
We focus on Inference-time attacks.
Attack Optimization:
\(\displaystyle \max_{\delta} l_{cls}(f_{\theta}(x'), y)\) such that \(\displaystyle \Vert x - x' \Vert \lt \epsilon\)
How to solve this optimization?
Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM)
For \(\displaystyle p=\infty\):
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
\delta_{FGSM} &= \max_{\Vert \delta \Vert \leq \epsilon} \lt \nabla l(f_{\theta}(x), y), \delta\gt \\
&= \epsilon sign(\nabla l(f_{\theta}(x), y))
\end{aligned}
\)
Pros:
- Fast because it is a one-step attack.
Projected Gradient Descent (PGD)
This is an iterative attack using gradient descent.
- Initalize \(\displaystyle x^(0) = x\)
- At each iteration, calculate \(\displaystyle \tilde{x}^{(t+1)} = x^{(t)} + \eta g^{(t)}\).
- Then project back into the ball \(\displaystyle x^{(t+1)} = \pi(\tilde{x}^{(t+1)}\).
- For \(\displaystyle l_{\infty}\), just do a element-wise clamp: \(\displaystyle x^{(t+1)} = clip(\tilde{x}^{(t+1)}, x - \epsilon, x + \epsilon)\)
In general, PGD > FGSM.
Alternative formulation
\(\displaystyle \min \Vert \delta \Vert\) such that \(\displaystyle f_{\theta}(x + \delta) = t \neq c^*\)
Lagrange dual form:
\(\displaystyle \min \Vert \delta \Vert - \lambda l_{cls}(f_{\theta}(x + \delta, y=c^*)\)
Adversarial Training
\(\displaystyle \min_{\theta} E \left[ \max_{x'} l_{cls}(f_{\theta}(x'), y) \right]\)
How to solve it?
- Inner max = attack problem (PGD)
- Outer max = gradient descent
Other heuristic/emperical defenses
Beginning of Lecture 9, Sept. 29 2020
ICLR 2018: 6-7 empirical defenses
Athalye et al (ICML 2018) show that obfuscated/masked gradients provide a false sense of security.
Such defenses can be easily broken using adaptive attacks. Obfuscated gradients provide shattered gradients (e.g. non-differentiable op) or stochastic gradients (e.g. randomized network).
- How to identify obfuscated or masked gradients?
Check the following:
- One step attack > iterative attack.
- Black-box attack > white-box attack.
- Unbounded attack (i.e. \(\displaystyle \rho\) can go to infinity) does not yield 100% success rate.
- Increasing attack budget doesn't increase the success rate.
If any of the above are true then your defense may be based on obfuscated or masked gradients.
- How to attack defenses using gradient masking?
- Defense based on adding a non-differentiable operator:
Example 1:
\(\displaystyle \hat{f}(x) = f(g(x))\) with g non-diff and non smooth.
In the attack, just use g(x)
Example 2:
Defense uses randomized classifier or stochastic gradients
Just take the expectation over the randomization.
Are adversarial examples inevitable?
- Notations
\(\displaystyle S^{d-1} = \{x \in \mathbb{R} \mid \Vert x \Vert = 1\}\)
Let the geodesic distance be denoted by \(\displaystyle d_{g}\).
This is the length of the shortest path on the sphere.
On sphere: \(\displaystyle d_{\infty}(x, x') \leq d_{2}(x, x') \leq d_{g}(x, x')\).
Classification problem: \(\displaystyle \{1,..., C\} = [c]\) labels.
Each class has a density function \(\displaystyle \rho_{c}\) which is bounded.
Let \(\displaystyle U_c = \sup_{x} \rho_c(x)\) be the largest density we can get.
The \(\displaystyle \epsilon\)-expansion of A:
\(\displaystyle A(\epsilon, d) = \{x \mid d(x,z)\leq \epsilon \text{ for some } z \in A\}\).
- Isoperimetric Inequality
Of all closed surfaces that encloses a unit volume, the sphere has the smallest surface.
Very intuitive but difficult to prove. (Osserman et al 1976)
- Lemma (Lerg & Pellegrino 1951, simplified by Talagrand 1995)
Consider a subset \(\displaystyle A \subset S^{d-1} \subset \mathbb{R}^n\) with normalized measure \(\displaystyle \mu_1(A) \geq 1/2\). Using the geodesic metric, the \(\displaystyle \epsilon\)-expansion \(\displaystyle A(\epsilon)\) is at least as large as the \(\displaystyle \epsilon\)-expansion of a half sphere.
- Lemma (Milman & Schechtman 1986)
\(\displaystyle A(\epsilon) \geq 1 - (\frac{\pi}{8})^{1/2} \exp(-\frac{d-1}{2} \epsilon^2)\)
As d goes to infinity, the right hand side goes to 1.
In a high-dimensional space, an epsilon expansion will cover almost the entire area.
- Theorem
c-class classification
\(\displaystyle \rho_c, u_c\)
\(\displaystyle v_c=\delta_{n-1} * u_c\) is the max density relative to uniform density.
\(\displaystyle f_c = \mu_1 \{x \mid C(x)=c\}\) is the area where the classifier \(\displaystyle C\) classifies as class c.
Pick a class \(\displaystyle f_c \leq \frac{1}{2}\).
Sample x from \(\displaystyle \rho_c\).
Either x is misclassified or x has an \(\displaystyle \epsilon\)-adversarial example.
One of these will happen with probability \(\displaystyle 1-v_c (\frac{\pi}{8})^{1/2} \exp^{- ((d-1)/2) \epsilon^2}\)
Proof:
Consider the region with the correct classification: \(\displaystyle R=\{x \mid c(x)=c\). Here \(\displaystyle u(R) = f_c \leq 1/2\).
Consider the compliment \(\displaystyle R^c\). \(\displaystyle u_1(R^c) \geq \frac{1}{2}\).
- Lemma
\(\displaystyle A \subset [0, 1]^d\) with \(\displaystyle vol(A) \geq \frac{1}{2}\)
\(\displaystyle vol(A(\epsilon g d p)) \geq 1 - \frac{\exp(-2 \pi d^{1-(2/p^2)\epsilon^2})}{2 \pi \epsilon d^{1/2 - 1/p^2}}\)
For l2 p>=2, \(\displaystyle p \geq 2\), \(\displaystyle vol(A(\epsilon g d p)) \geq 1 - \frac{\exp(-2 \pi \epsilon^2)}{2 \pi \epsilon}\)
For p=2, the diameter of the hypercube is \(\displaystyle O(\sqrt{d})\).
For p=infinity, the diameter of the cube is 1.
This shows if you pick a random sample, there is a high probability of it being misclassified or there being an adversarial example within epsilon.
- Are adversarial examples inevitable in practice?
This is an ill-posed question.
It depends on the data distribution, threat model, and hypothesis class.
Provable Defenses
There are 3 types of Lp defenses:
- Curvature-based defenses
- IBP and Convex defenses
- Randomzied smoothing
For Non-Lp
- Patch Threat
- Sparse Threat
- Wasserstein Threat
Randomized Smoothing
A smoothed classifier: \(\displaystyle \bar{f}(x) = E_{\epsilon}[f(x+\epsilon)]\). The idea is that the decision boundary becomes smoother.
Gaussian Smoothing for L2 attacks:
- Theorem (Cohen et al., 2019)
No adversarial example exists within the radius:
\(\displaystyle \frac{\sigma}{2}\left(\Phi^{-1}(p_1(x))-\Phi^{-1}(p_2(x))\right)\)
The proof is based on Neyman & Pearson lemma.
- Theorem (Levine, Singla, F2019, Salman et al 2019)
\(\displaystyle \Phi^{-1}(\bar{f}(x))\) is Lipschitz with constant \(\displaystyle 1/\sigma\)
The worst g is a stepwise function. Then \(\displaystyle \Phi^{-1}(\bar{g})\) is a linear function.
For L2 attacks, you can use Gaussian noise. For L1 attacks, you can use Laplace noise.
- Theorem (KLGF, ICML 2020)
Using any symmetric i.i.d. smoothing, \(\displaystyle r_{p}^* \leq \frac{\sigma}{2 \sqrt{2} d^{1/2 - 1/p}}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-p_1(x)}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{p_2(x)}}\right)\)
If we use Gaussian smoothing against Lp attacks, we get:
\(\displaystyle r_p = \frac{\sigma}{2d^{1/2 - 1/p}}\left( \Sigma^{-1}(p_1(x)) - \Sigma^{-1}(p_2(x)) \right)\)
This shows that Gaussian smoothing is optimal (up to a constant) within i.i.d. smoothing distributions against Lp attacks.
Sparse Threat
Here the adversary can change up to \(\displaystyle \rho\) pixels in the image.
The idea is to classify each example based on only k random pixels in the image. This is performed several times and the a voting scheme determines the final label.
- Theorem (Levine, F. AAAI 2020)
For inputs \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle x'\) with \(\displaystyle \Vert x - x' \Vert_{l_0} \leq \rho\), for all i \(\displaystyle \vert p_i(x) - p_i(x')\vert \leq \delta\) where \(\displaystyle \delta = 1 - \frac{\binom{d-\rho}{k}}{\binom{d}{k}}\).
Robustness vs Accuracy Trade-off:
Increasing \(\displaystyle k\) boosts classification accuracy but also increases \(\displaystyle \Delta\).
Relationship between Threat Models
Use a neural perceptual threat model to approximate the true perceptual distance.
Use LPIPS as \(\displaystyle d_{neural}(x, x') = \Vert \phi(x) - \phi(x') \Vert\) where \(\displaystyle \phi\) are normalized feature maps.
Our attack optimization is now:
\(\displaystyle
\begin{aligned}
\max_{x'} &l_{cls}(f(x'), y)\\
& d_{neural}(x, x') \leq \rho
\end{aligned}
\)
From this, we get Perceptual Projected Gradient Descent (PPGD) and Lagrangian Perceptual Attacks (LPA).
We also get Perceptual Adversarial Training (PAT).
Misc
Resources
<templatestyles src="Reflist/styles.css" />
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Chaoyue Liu, Libin Zhu, Mikhail Belkin (2020). Toward a theory of optimization for over-parameterized systems of non-linear equations: the lessons of deep learning https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.00307
- ↑ Simon S. Du, Xiyu Zhai, Barnabas Poczos, Aarti Singh (2019). Gradient Descent Provably Optimizes Over-parameterized Neural Networks (ICLR 2019) https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.02054
- ↑ Daniel Soudry, Elad Hoffer, Mor Shpigel Nacson, Suriya Gunasekar, Nathan Srebro (2018) The Implicit Bias of Gradient Descent on Separable Data The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2018 https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10345
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chiyuan Zhang, Samy Bengio, Moritz Hardt, Benjamin Recht, Oriol Vinyals (2017) Understanding deep learning requires rethinking generalization (ICLR 2017) https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.03530
- ↑ Mikhail Belkin, Daniel Hsu, Siyuan Ma, Soumik Mandal (2019) Reconciling modern machine learning practice and the bias-variance trade-off (PNAS 2019) https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.11118
- ↑ Yiding Jiang, Behnam Neyshabur, Hossein Mobahi, Dilip Krishnan, Samy Bengio (2019) Fantastic Generalization Measures and Where to Find Them https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.02178
