Parallel Algorithms: Difference between revisions
| Line 550: | Line 550: | ||
The internal node will be <math>(a*l+b) \times (c*r+d)</math> where <math>\times</math> is either addition or multiplication.<br> | The internal node will be <math>(a*l+b) \times (c*r+d)</math> where <math>\times</math> is either addition or multiplication.<br> | ||
If we delete one leaf and it's parent (stem), we will modify these variables of the stem's parent. | If we delete one leaf and it's parent (stem), we will modify these variables of the stem's parent. | ||
===Tree Binarization=== | |||
;Note: This is not in the classnotes, but has been covered in exams. | |||
To apply the above techniques to general trees or k-ary trees, you should binarize your k-ary tree.<br> | |||
This is done as follows: | |||
* Suppose node <math>x</math> has <math>n > 2</math> children | |||
* Select one child to keep | |||
* Create a node <math>x'</math> | |||
* Move all <math>n-1</math> children to <math>x'</math> | |||
* Set child <math>x'</math> to be a child of <math>x</math> | |||
==Graph Connectivity== | ==Graph Connectivity== | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 30 April 2020
Parallel Algorithms notes from CMSC751 with Uzi Vishkin.
This class is based on his book Thinking in Parallel Some Basic Data-Parallel Algorithms and Techniques
XMT Language
XMTC is a single-program multiple-data (SPMD) extension of C.
- Spawn creates threads
- Threads expire at Join
$represents the number of the threadPS Ri Rjis an atomic prefix sum- Stores Ri + Rj in Ri
- Stores the original value of Ri in Rj
int x = 0;
// Spawn n threads
spawn(0, n-1) {
int e = 1;
if (A[$] != 0) {
// Sets e=x and increments x
ps(e,x);
}
}
Models
PRAM
Parallel Random-Access Machine/Model
You're given n synchronous processors each with local memory and access to a shared memory.
Each processor can write to shared memory, read to shared memory, or do computation in local memory.
You tell each processor what to do at each time step.
Types of PRAM
- exclusive-read exclusive-write (EREW)
- concurrent-read exclusive-write (CREW)
- concurrent-read concurrent-write (CRCW)
- Arbitrary CRCW - an arbitrary processor writing succeeds
- Priority CRCW - the lowest numbered processor writing succeeds
- Common CRCW - writing succeeds only if all processors write the same value
Drawbacks
- Does not reveal how the algorithm will run on PRAMs with different number of proc
- Fully specifying allocation requires an unnecessary level of detail
Work Depth
You provide a sequence of instructions. At each time step, you specify the number of parallel operations.
WD-presentation Sufficiency Theorem
Given an algorithm in WD mode that takes \(\displaystyle x=x(n)\) operations and \(\displaystyle d=d(n)\) time, the algorithm can be implemented in any p-processor PRAM with \(\displaystyle O(x/p + d)\) time.
- Notes
- Other resources call this Brent's theorem
- \(\displaystyle x\) is the work and \(\displaystyle d\) is the depth
Speedup
- A parallel algorithm is work-optimal if W(n) grows asymptotically the same as T(n).
- A work-optimal parallel algorithm is work-time-optimal if T(n) cannot be improved by another work-optimal algorithm.
- If T(n) is best known and W(n) matches it, this is called linear-speedup
NC Theory
Nick's Class Theory
- Good serial algorithms: Poly time
- Good parallel algorithm: poly-log \(\displaystyle O(\log ^c n)\) time, poly processors
Technique: Balanced Binary Trees
Example Applications:
- Prefix sum
- Largest element
- Nearest-one element
- Compaction
- Inputs
- Array A[1..n] of elements
- Associative binary operation, denoted * (e.g. addition, multiplication, min, max)
- Outputs
- Array B containing B(i) = A(1) * ... * A(i)
- Algorithm
\(\displaystyle O(n)\) work and \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time
for i, 1 <= i <= n pardo
B(0, i) = A(i)
// Summation step up the tree
for h=1 to log n
B(h, i) = B(h-1, 2i-1) * B(h-1, 2i)
// Down the tree
for h=log n to 1
if i even, i <= n/2^h
C(h, i) = C(h+1, i/2)
if i == 1
C(h, i) = B(h, i)
if i odd, 3 <= i <= n/2^h
C(h, i) = C(h+1, i/2) * B(h, i)
return C(0, :)
Technique: Merge Sorting Cluster
Technique: Partitioning
- Merging: Given two sorted arrays, A and B, create a sorted array C consisting of elements in A and B
- Ranking: Given an element x, find \(\displaystyle Rank(x, A) = i\) defined such that \(\displaystyle A(i) \leq x \leq A(i+1)\)
- Note the book sometimes uses \(\displaystyle Rank(i,B)\) to denote \(\displaystyle Rank(A(i), B)\).
- Equivalence of Merging and Ranking
- Given an algorithm for merging, we know A(i) belongs in C(j) so Rank(A(i), B) = j-i
- Given an algorithm for ranking, we get A(i) belongs in C(j) where j = Rank(A(i), B) + i
- Naive algorithm
Apply binary search element wise on concurrent read system. O(log n) time, O(nlog n) work
for 1 <= i <= n pardo Rank(A(i), B) Rank(B(i), A)
- Partitioning paradigm
Input size: n
- Partition the input into p jobs of size approx. n/p
- Do small jobs concurrently using a separate (possibly serial) algo for each.
Example: Total work O(n), total time O(log n)
// Partitioning for 1 <= i <= p pardo b(i) = Rank((n/p)(i-1)+1, B) a(i) = Rank((n/p)(i-1)+1, A) // Total slice size is <= 2n/p. Total 2p slices. // E.g. slice size is 2 * log(n) if p=n/log(n). // Work for 1 <= i <= p pardo k = ceil(b(i)/(n/p)) * (n/p) merge slice A[(n/p)(i-1)+1:min(a(i), end_a] and B[b(i):end_b]
- Notes
- We do not need to compute A_end or B_end. Just continue merging until we hit some index where (i % x)=0 in A or B.
Techinque: Divide and Conquer
- Merge Sort
Input: Array A[1..n]
Complexity:
Time: \(\displaystyle T(n) \leq T(n/2) + \alpha \log n\)
Work: \(\displaystyle T(n) \leq 2 * T(n/2) + \beta n\)
Time \(\displaystyle O(\log^2 n)\). Work: \(\displaystyle O(n \log n)\)
MergeSort(A, B):
if n == 1
return B(1) = A(1)
call in parallel:
MergeSort(A[1:n/2], C[1:n/2])
MergeSort(A[n/2+1:n], C[n/2+1:n])
Merge C[1:n/2] and C[n/2:n] using O(log n) algorithm
Technique: Informal Work-Depth (IWD) and Accelerating Cascades
Technique: Accelerating Cascades
Consider: for problem of size n, there are two parallel algorithms.
- Algo A: \(\displaystyle W_1(n)\) work, \(\displaystyle T_1(n)\) time
- Algo B: Work \(\displaystyle W_2(n) \gt W_1(n)\). Time \(\displaystyle T_2(n) \lt T_1(n)\). Faster but less efficient.
Assume Algo A is a "reducing algorithm"
We start with Algo A until the size is below some threshold. Then we switch to Algo B.
E.g.
- Algo 1 runs in \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) iterations each taking \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work. Each iteration reduces the size to (3/4)m.
- Algo 2 runs in \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n\log n)\) work.
- Run Algo 1 for \(\displaystyle O(\log \log n)\) rounds then run algo 2.
- Total time is \(\displaystyle O(\log n \log \log n)\) and work is \(\displaystyle O(n)\)
Problem: Selection
- Algorithm 1
- Partition elements into rows of \(\displaystyle \log n\) size
- For each row, find the median within the row
- Find the median of medians (MoM) in \(\displaystyle O(n)\)
- Put all rows with median <= MoM above and all rows with median >= Mom below
- Now \(\displaystyle m/4\) elements are smaller and \(\displaystyle m/4\) are larger
- Known as the reducing lemma
This algorithm solves the selection problem in \(\displaystyle O(\log^2 n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work.
- Accelerating Cascades
- What we have:
- Algorithm 1 has \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) iterations.
- Each iteration reduces a size m instance in \(\displaystyle O(\log m)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(m)\) work to an instance of size \(\displaystyle \leq 3m/4\)
- Algorithm 2 runs in \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n \log n)\) work.
- Step 1: Use algo 1 to reduce from n to \(\displaystyle n / \log n\)
- Step 2: Apply algorithm 2
Informal Work-Depth (IWD)
At each time unit there is a set containing a number of instructions to be performed concurrently.
Integer Sorting
There is a theorem that sorting with only comparisons is worst case at least \(\displaystyle O(n\log n)\)
Input: Array A[1..n], integers are range [0..r-1]
Sorting: rank from smallest to largest
Assume n is divisible by r (\(\displaystyle r=\sqrt{n}\))
Algorithm
- Partition A into n/r subarrays \(\displaystyle B_1,...,B_{n/r}\)
- Sort each subarray separately using serial bucket sort (counting sort)
- Compute number(v,s) # of elements of value v in \(\displaystyle B_s\) for \(\displaystyle 0\leq v \leq r-1\) and \(\displaystyle 1 \leq s \leq n/r\)
- Compute serial(i) = # of elements in the block \(\displaystyle B_s\) such that A(j)=A(i) and \(\displaystyle j \lt i \) \(\displaystyle 1 \leq j \neq n\)
- Run prefix sum on number(v,1),number(v,2),...,number(v,n/r) into ps(v,1), ps(v,2),..., ps(v,n/r)
- Compute prefix sums of cardinality(0),.., cardinality(r-1) into global_ps(0),...,global_ps(r-1)
- The rank of element \(\displaystyle i\) is \(\displaystyle 1+serial(i)+ps(v,s-1)+global_ps(v-1)\)
Complexity
- Step 1:\(\displaystyle T=O(r),\;W=O(r)\) per subarray.
- Total: \(\displaystyle T=O(r),\; W=O(n)\)
- Step 2: \(\displaystyle r\) computations each \(\displaystyle T=O(\log(n/r)),\; W=O(n/r)\)
- Total \(\displaystyle T=O(\log n),\; W=O(n)\)
- Step 3: \(\displaystyle T=O(\log r),\; W=O(r)\)
- Step 4: \(\displaystyle T=O(1)\; W=O(n)\)
- Total: \(\displaystyle T=O(r + \log n),\; W=O(n)\)
- Notes
- Running time is not poly-log
Theorems
- The integer sorting algorithm runs in \(\displaystyle O(r+\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
- The integer sorting algorithm can be applied to run in time \(\displaystyle O(k(r^{1/k}+\log n))\) and work \(\displaystyle O(kn)\)
Radix sort using the basic integer sort (BIS) algorithm.
If your range is 0 to n and and your radix is \(\displaystyle \sqrt{n}\) then you will need \(\displaystyle log_{\sqrt{n}}(r) = 2\) rounds.
2-3 trees; Technique: Pipelining
Dictionary: Search, insert, delete
Problem: How to parallelize to handle batches of queries
2-3 tree
A 2-3 tree is a rooted tree which has the properties:
- Each node has 2-3 ordered children
- For any internal node, every directed path to a leaf is the same length
Types of queries:
- search(a)
- insert(a)
- delete(a)
Serial Algorithms
- Deletion: discard(a)
- Delete connection between a and parent of a
- If parent has 1 child
- If parent's sibling has 2 children, move child to sibling and discard(parent)
- If parent's sibling has 3 children, take one child from sibling
Parallel Algorithms
Assume concurrent read model
- Insert: Suppose we want to insert sorted elements \(\displaystyle c_1,...,c_k\) into a tree with n elements.
- Insert element \(\displaystyle c_{k/2}\).
- Then insert in parallel \(\displaystyle (c_1,...,c_{k/2-1})\) and \(\displaystyle (c_{k/2+1},...,c_k)\)
- Time is \(\displaystyle O(\log k \log n)\) using \(\displaystyle k\) processors.
- Deletion: Suppose we want to delete sorted elements \(\displaystyle c_1,...,c_k\)
- Backwards Insertion
- for t=0 to \(\displaystyle \log k\)
- if \(\displaystyle i \equiv 2^t (\operatorname{mod}2^{t+1})\)
- discard(c_i)
- if \(\displaystyle i \equiv 2^t (\operatorname{mod}2^{t+1})\)
- Time is \(\displaystyle O(\log n \log k)\) without pipelining
- With pipelining, complexity is \(\displaystyle O(\log n + \log k)\)
Pipelining
- There are \(\displaystyle \log k\) waves of the absorb procedure.
- Apply pipelining to make the time \(\displaystyle O(\log n + \log k)\)
Maximum Finding
Given an array A=A(1),...,A(n), find the largest element in the array
Constant time, \(\displaystyle O(n^2)\) Work
- Compare every pair of elements in A[1...n]
for i=1 to n pardo
B(i) = 0
for 1 <= i,j <= n pardo
if A(i) <= A(j) and i < j
B(i) = 1
else
B(j) = 1
for 1 <= i <= n pardo
if B(i) == 0
A(i) is the max
\(\displaystyle O(\log \log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n\log \log n)\) work algorithm
- Split A into \(\displaystyle \sqrt{n}\) subarrays
- Find the max of each subarray recursively
- Find the max of all subarrays in \(\displaystyle O(n)\) using the constant time algo
Complexity
- \(\displaystyle T(n) \leq T(\sqrt{n}) + c_1\)
- \(\displaystyle W(n) \leq \sqrt{n}W(\sqrt{n}) + c_2 n\)
- \(\displaystyle T(n) = O(\log \log n)\), \(\displaystyle W(n) = O(n\log \log n)\)
\(\displaystyle O(\log \log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
- Step 1: Partition into blocks of size \(\displaystyle \log \log n\). Then we have \(\displaystyle n/ \log \log n\) blocks.
- Apply serial linear time algorithm to find maximum of each block
- \(\displaystyle O(\log \log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work.
- Step 2: Apply doubly log algorithm to \(\displaystyle n / \log \log n\) maxima.
- \(\displaystyle O(\log \log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work.
Random Sampling
Maximum finding in \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work with very high probability
- Step 1: Using aux array B of size \(\displaystyle b^{7/8}\). Independently fill with random elements from A
- Step 2: Find the max \(\displaystyle m\) in array B in \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
- Last 3 pulses of the recursive doubly-log time algorithm:
- Pulse 1: B is partitioned into \(\displaystyle n^{3/4}\) blocks of size \(\displaystyle n^{1/8}\) each. Find the max of each block.
- Pulse 2: \(\displaystyle n^{3/4}\) maxima are partitioned into \(\displaystyle n^{1/2}\) blocks of size \(\displaystyle n^{1/4}\) each.
- Pulse 2: Find the max m of \(\displaystyle n^{1/2}\) maxima in \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work.
- Step 3: While there is an element larger than m, throw the new element into an array of size \(\displaystyle n^{7/8}\).
- Compute the maximum of the new array.
- Complexity
- Step 1 takes \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n^{7/8})\) work
- Step 2 takes \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
- Each time Step 3 takes \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
- With high probability, we only need one iteration (see theorem below) so the time is \(\displaystyle O(1)\) and work is \(\displaystyle O(n^{7/8})\)
Theorem 8.2
The algorithm find the maximum among \(\displaystyle n\) elements. With high probability it runs in \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work. The probability of not finishing in the above time is \(\displaystyle O(1/n^c)\).
List Ranking Cluster
Techniques: Euler tours, pointer jumping, randomized and deterministic symmetry breaking
Rooting a tree
Technique: Euler tours
- Inputs
- Vector of vertices which point to an index in edges
- Vector of edges e.g. (1,2)
- Vector of pointers to identical edges e.g. index of (1,2) -> index of (2,1)
- A vertex \(\displaystyle r\)
- Goal
- Select a direction for each edge to make our graph a tree with root \(\displaystyle r\)
- Algorithm
- Step 1: For every edge \(\displaystyle (u,v)\), add two edges \(\displaystyle u \rightarrow v\) and \(\displaystyle v \rightarrow u\)
- Step 2: For every directed edge \(\displaystyle u \rightarrow v\), set a pointer to another directed edge from \(\displaystyle v\), \(\displaystyle next(u \rightarrow v)\)
- If our edge is 1 -> 2, then the next edge is the immediate next edge of edge 2->1 in our edges array
- If edge 2 -> 1 is the last edge coming out of 2, then the next edge is the first edge coming out of 2
- Now we have an euler cycle (or euler tour) among the edges
- Step 3: \(\displaystyle next(u_{r,1} \rightarrow r) = NIL \)
- Step 4: Apply a list ranking algorithm to the edges.
- Step 5: Delete the edge between every two vertices with the lower ranking
- Notes
- Every step except 4, list ranking, is a local operation which is constant time and linear work
- Requires a list ranking algorithm
Preorder Numbering
Define: tree-edges point away from root, non-tree edges point to root
- Step 1: For every edge pardo, if e is a tree edge, distance(e) = 1 else distance(e) = 0
- Step 2: List ranking
- Step 3: For every edge e: u->v, preorder(v) = n-distance(e) + 1
Technique: Pointer Jumping
List Ranking
Input: A dense array A. For each element except first, we have a node pointing its successor in the array.
Each element, except last, is the successor of one element.
rank(i)=0 for last, rank(i) = rank(next(i)) + 1 for the rest
The last element we call the "cashier".
Idea:
At iteration 0, node i points to node i+1
At iteration 1, node i points to node i+2
At iteration 2, node i points to node i+4...
for i 1 <= i <= n pardo:
if next[i] == NIL then distance[i] = 0 else distance[i] = 1
for k = 1 to log g:
distance[i] = distance[i] + distance[next[i]]
next[i] = next[next[i]]
Correctness:
- Each element will eventually point to the cashier
- Distance will always be correct
- If next[i] = NIL then distance is to the cashier
- Otherwise the distance is \(\displaystyle 2^k\)
Complexity: \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n\log n)\) work
Work-optimal List Ranking
- From our list A, pull a subset S with uniform density and sparcity
- Remove S from A, creating a new subset \(\displaystyle A-S\).
- For each element i in \(\displaystyle S\), fix the next and distance of prev(i)
- Run compaction
- Recurse on \(\displaystyle A-S\) until size is \(\displaystyle \leq n/\log n\). Then use pointer jumping.
- Add \(\displaystyle S\) back to \(\displaystyle A-S\)
- Complexity
With high probability:
- \(\displaystyle O(log (n) log log (n)) time\)
- \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work
Randomized Symmetry Breaking
for i 1 <= i <= n pardo
with equal probability R(i) = head or tail
if R(i) == HEAD and R(next(i))==Tail
s(i) = 0
else
s(i) = 1
Deterministic Symmetry Breaking
- Assign each element a unique tag, such as the index in the array
- Convert the tag to binary. For each element i, tag(i)!=tag(next(i)).
- Let k be the index of the rightmost bit (where 0 is the rightmost bit) differing between tag(i) and tag(next(i))
- Let b be the bit in tag(i) differing from tag(next(i))
- Set the new tag to
(k<<1) + b
This algorithm takes \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work per iteration.
If the range of tags before the iteration are \(\displaystyle [0,...,n-1]\) then the range of tags after will be \(\displaystyle [0,...,2*\log n - 1]\).
r-ruling set
An r-ruling set is a subset \(\displaystyle S\) of a linked list satisfying two properties:
- Uniform Density If node \(\displaystyle i\) is not in S, then one of the \(\displaystyle r\) nodes following i will be in \(\displaystyle S\)
- Uniform Sparcity If node \(\displaystyle i\) is in \(\displaystyle S\) then node \(\displaystyle next(i)\) is not in \(\displaystyle S\)
- Algorithm
The following algorithm gives us an r-ruling set with \(\displaystyle r=2*\log n - 1\)
- Apply the deterministic coin tossing algorithm to give each element a tag in \(\displaystyle [0,...,2*\log n - 1]\)
- For each element i in parallel, if i is a local maximum then add it to \(\displaystyle S\)
Tree Contraction
Serial Rake
Consider a node y with left leaf x and right subtree z.
Rake(x) would delete x and y, setting parent(z) to the previous parent of y.
Observation 1: Applying a rake to a binary tree yields a binary tree
Parallel Rake
Rake all leaves such that:
- No two leaves have the same parent (stem)
- The parent of a stem cannot be the stem of another leaf
Observation 2: Applying a legal parallel rake to a binary tree yields a binary tree
- Parallel Rake Contraction Scheme
Apply legal parallel rakes until the tree becomes a 3-node binary tree
- Parallel Rake Contraction Algorithm
- Step 1
- Number leaves according to a DFS using the Euler tour algorithm.
Observation 3:
Consider the leaves whose number is odd, L.
Let S consist of the stems of those leaves L.
Then each node in S can be adjacent to at most one other node in S.
Proof: See the classnotes
- Step 2
- Let \(\displaystyle S_1\) be nodes in \(\displaystyle S\) whose parents are not in \(\displaystyle S\).
- Let \(\displaystyle L_1\) be leaves in \(\displaystyle L\) whose parents are in \(\displaystyle S_1\).
- Apply parallel rakes to leaves in \(\displaystyle L_1\), unless the parent is the root.
- Apply parallel rakes to leaves in \(\displaystyle L - L_1\), unless the parent is the root.
- Repeat Step 2 until the tree is a 3-node binary tree
Complexity
Step 2 takes \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) rounds. Each leaf gets raked only once.
In total we take \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n)\) work.
Evaluating an Arithmetic Expression
Consider a binary tree where each internal node is an operator:
Either addition or multiplication.
Each leaf is a number
Assign each internal node 4 numbers: a,b,c,d
These are initialized to (1,0,1,0)
The internal node will be \(\displaystyle (a*l+b) \times (c*r+d)\) where \(\displaystyle \times\) is either addition or multiplication.
If we delete one leaf and it's parent (stem), we will modify these variables of the stem's parent.
Tree Binarization
- Note
- This is not in the classnotes, but has been covered in exams.
To apply the above techniques to general trees or k-ary trees, you should binarize your k-ary tree.
This is done as follows:
- Suppose node \(\displaystyle x\) has \(\displaystyle n \gt 2\) children
- Select one child to keep
- Create a node \(\displaystyle x'\)
- Move all \(\displaystyle n-1\) children to \(\displaystyle x'\)
- Set child \(\displaystyle x'\) to be a child of \(\displaystyle x\)
Graph Connectivity
Preliminaries
For parallel algorithms, a graph can be represented as an incidence list or an adjacency matrix.
An incidence list is an array of edges ordered by the starting point and ending point. An array of vertices point to the starting index of the vertices outgoing edges within the edge array. I.e. edges with index [v[i], v[i+1]) start at vertex i
Definitions:
- Pointer Graph
- Supervertices
- The supervertex graph
- Hookings
- Parallel pointer jumping
A first connectivity algorithm
The first connectivity algorithm consists of \(\displaystyle \log(n)\) iterations of the following two steps:
- Hookings - Each root hooks itself the the minimal adjacent root. If there are no adjacent stars, then this rooted star quits.
- Parallel pointer jumping - Each vertex performs pointer jumping until every vertex points to the root, forming a rooted star.
- Theorems
- The pointer graph always consists of rooted trees.
- After \(\displaystyle \log n\) iterations, all vertices are contained in rooted stars that quit.
- Each connected component is represented by a single rooted star.
- Complexity
- We need \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) iterations
- Hookings take \(\displaystyle O(1)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n+m)\) work
- Pointer jumping takes \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n\log n)\) work
- For adjacency matrix, in total we need \(\displaystyle O(\log^2 n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n^2\log n)\) work since we have a processor per \(\displaystyle n^2\) possible edges.
- For incidence lists, we need \(\displaystyle O(\log^2 n)\) time and \(\displaystyle O(n\log^2 n + m\log n)\) work since we have a processor per edge.
A second connectivity algorithm
The second connectivity algorithms consists of \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) iterations.
Each iteration takes constant time.
- Probe quitting: each rooted star whose supervertex is not adjacent to any other quits
- Hooking on smaller: each rooted star hooks onto a smaller vertex of another supervertex which is not a leaf
- Note that this is not unique. Requires arbitrary CRCW.
- Hooking non-hooked-upon: every rooted star not hooked upon in step 2 hooks to another vertex in another supervertex which is not a leaf
- Parallel pointer jumping: one round of parallel pointer jumping
- Theorems
- The pointer graph always consists of rooted trees.
- For every vertex which is not a leaf, \(\displaystyle D(v) \leq v\)
- Complexity
- Time \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\)
- Work \(\displaystyle O((n+m)\log n)\)
- Notes
- Without step 3, the algorithm will run in \(\displaystyle O(n)\) time instead of \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) but the result will be valid.
- In step 2, you can hook rooted trees in addition to rooted stars for better empirical performance
Minimum Spanning Forest
The MSF Theorem
Let \(\displaystyle G(V,E)\) be a weighted graph and let \(\displaystyle U\) and \(\displaystyle V-U\) be two non-empty subsets of \(\displaystyle V\). Consider set \(\displaystyle H=\{(u,v) \mid u \in U, v \in V\}\) of edges connecting points in \(\displaystyle U\) and \(\displaystyle V\). If \(\displaystyle e\) is the edge of minimum weight in \(\displaystyle H\), then \(\displaystyle e\) is in the MSF of \(\displaystyle G\)
A first MSF algorithm
- Sort the edges by weight. Assign a processor to each edge. Using a priority CRCW, the edge with minimum weight will take priority during writes.
Each round consists of hooking and \(\displaystyle \log n\) rounds of parallel pointer jumping
- Each root find the minimum weight edge to another supervertex and hooks itself to that root.
- This is automatic from the priority CRCW.
A second MSF algorithm
We replace steps 2 and 3 in the connectivity algorithm with the simple rule:
- We hook rooted stars using the edge with the smallest weight.
- Notes
- The progression of edge weights up the tree are monotonically increasing so there are no cycles
Tricks
Removing duplicates in an array
Assume you have an Arbitrary CRCW
- Given array A of size n with entries 0 to n-1
- For each entry pardo
- Write B[A[i]] == i
- Only one write will succeed for each unique A[i]
- Check if B[A[i]] == i
Compaction of an \(\displaystyle n^2\) array with \(\displaystyle \leq n\) elements in \(\displaystyle O(\log n)\) time
- Split our \(\displaystyle n^2\) array to n subarrays, each of size \(\displaystyle n\)
- Run \(\displaystyle n\) parallel compactions on each subarray
- Perform one compaction on the size of each subarray
- Compact all elements using (total size of prev subarrays + position in current subarray)
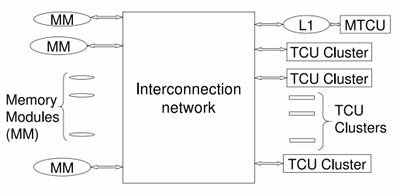
Hardware/Architecture
Models for Advancing PRAM and Other Algorithms into Parallel Algorithms for PRAM
- MTCU - Master Thread Control Unit - runs in serial mode
- TCU Cluster - Thread Control Unit
- Procedure
- Spawn broadcasts your spawn code in the block to every thread control unit (TCU).
- Data is shared through the interconnection network
- Performance Penalty
\(\displaystyle \text{Execution Depth} = \text{Computation Depth} + LSRTM \times R + QD\)
- \(\displaystyle LSTRM\) - length of sequence of round trips to memory
- \(\displaystyle R\) - time for round trip to memory
- \(\displaystyle QD\) - queuing delay
- If multiple threads access the same memory module, they are queued at the memory module
Resources
Textbooks
- Uzi Vishkin ENEE651/CMSC751 Classnotes
- Introduction to Parallel Algorithms (Joseph Jaja, textbook)
- Parallel Algorithms by Guy E. Blelloch and Bruce M. Maggs (CMU)