CUDA: Difference between revisions
Appearance
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
For example: | For example: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
# Install the runtime | |||
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-toolkit | conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-toolkit | ||
# | # Install development tools | ||
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-libraries-dev | conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-libraries-dev | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 15 June 2023
Installation
I suggest using conda to install cuda for version control your project.
Conda
See nvidia/cuda-toolkit and nvidia/cuda-libraries-dev
For example:
# Install the runtime
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-toolkit
# Install development tools
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-libraries-dev
Ubuntu
Details
# Set UBUNTU_VERSION to 2004 or 2204
UBUNTU_VERSION=$(lsb_release -sr | sed -e 's/\.//g')
# Add NVIDIA package repositories
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu${UBUNTU_VERSION}/x86_64/cuda-ubuntu${UBUNTU_VERSION}.pin
sudo mv cuda-ubuntu${UBUNTU_VERSION}.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600
sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu${UBUNTU_VERSION}/x86_64/3bf863cc.pub
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu${UBUNTU_VERSION}/x86_64/ /"
# Install NVIDIA driver and cuda.
sudo apt install nvidia-driver-515 cuda
# Reboot and check that the drivers are working with nvidia-smi
sudo reboot
# Install cudnn
sudo apt install libcudnn8 libcudnn8-dev
- Notes
- For machine learning, use Anaconda or Docker's CUDA since different versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch require different CUDA versions.
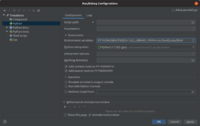
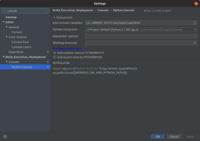
You may need to add LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64 to your environment variables.
You can also do this in PyCharm.
GCC Versions
nvcc sometimes only supports older gcc/g++ versions.
To make it use those by default, create the following symlinks:
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/gcc-6 /usr/local/cuda/bin/gccsudo ln -s /usr/bin/g++-6 /usr/local/cuda/bin/g++
Alternatively, you can use -ccbin and point to your gcc:
-ccbin /usr/local/cuda/bin/gcc
