Latex: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
\newcommand{\etal}{{\em et al. }} | \newcommand{\etal}{{\em et al. }} | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Bibliography== | |||
==Tikz== | ==Tikz== | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 2 December 2019
Typeset all of your papers using latex.
Installation
No Install
Use Overleaf to create latex documents in a web browser.
Partial Install
Download MikTex. It includes the TeXworks editor and will download packages as you use them. This will not take up as much disk space as a full install.
Full Install
Windows
Download TexLive. This is several gigabytes since it includes all the popular LaTex packages and takes a while to install. You'll also need an editor. I recommend installing Atom with the following packages:
latexfor calling the TexLive compilerlanguage-latexfor syntax highlightingpdf-viewfor viewing the compiled pdf.
Linux
sudo apt install texlive-full
Compile tex documents with
pdflatex [mydocument.tex]
Usage
Fancy Math Font
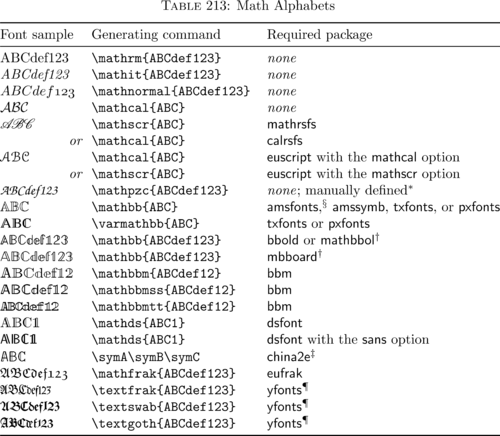
See this answer.
% Use mathbb for the set of reals R or the set of complex numbers C
% Requires amsfonts
\mathbb{R}
Spaces
See Reference
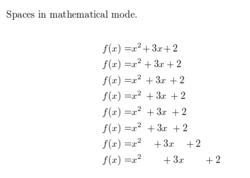
Spaces in mathematical mode.
\begin{align*}
f(x) =& x^2\! +3x\! +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2+3x+2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\, +3x\, +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\: +3x\: +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\; +3x\; +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\ +3x\ +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\quad +3x\quad +2 \\
f(x) =& x^2\qquad +3x\qquad +2
\end{align*}
Indents
Section
\hspace*{5mm}\begin{minipage}{\dimexpr\textwidth-5mm}
Indented Section
\end{minipage}
Programming
Latex is a turing complete language.
You can use if statements and for loops in latex.
Custom Commands
You can define your own commands using \newcommand
Custom Operators
Latex packages like amsmath come with operators such as \sin and \log.
To get normal text for custom functions like arcsin, use \operatorname{arcsin}.
Below are some potentially useful math operators.
\DeclareMathOperator{\Tr}{Tr}
\DeclareMathOperator{\VCdim}{VCdim}
\DeclareMathOperator{\sign}{sign}
\DeclareMathOperator{\rank}{rank}
\DeclareMathOperator{\argmin}{argmin}
\DeclareMathOperator{\argmax}{argmax}
Enumerate
Enumerate is used to make lists
Change the label
Reference
Add the option for the labels:
label=(\alph*)for letterslabel=(\Alph*)for upper-case letterslabel=(\roman*)for roman numerals.label=(\arabic*)for numbers
\usepackage{enumitem}
#...
\begin{enumerate}[label=(\alph*)]
\item an apple
\item a banana
\item a carrot
\item a durian
\end{enumerate}
Useful Commands
A list of potentially useful commands
\newcommand{\degree}{\ensuremath{^{\circ}} }
\newcommand{\etal}{{\em et al. }}
Bibliography
Tikz
Tikz is used to draw graphs and other shapes
Drawing over images
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[anchor=south west,inner sep=0] (image) at (0,0) {
\includegraphics[width=.9\linewidth]{my_image.png}
};<br />
\begin{scope}[x={(image.south east)},y={(image.north west)}]
\draw[black,ultra thick,rounded corners] (0.0,0.1) rectangle (0.3,0.5);
\draw[red,ultra thick,rounded corners] (0.5,0.1) rectangle (0.8,0.5);
% \draw[help lines,xstep=.1,ystep=.1] (0,0) grid (1,1);
% \foreach \x in {0,1,...,9} { \node [anchor=north] at (\x/10,0) {0.\x}; }
% \foreach \y in {0,1,...,9} { \node [anchor=east] at (0,\y/10) {0.\y}; }
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}
